Ethernet vs Wi-Fi: Which One is Better?
Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two main ways to connect your computer to the internet. While Wi-Fi has received significantly more attention in recent years, especially among consumers, due to its simplicity and flexibility, ethernet is still widely used in various other applications.
Even if Wi-Fi is significantly more popular, it isn’t strictly better. Both methods have their benefits and drawbacks. Wi-Fi’s popularity comes from its ease-of-use and flexibility, but an ethernet connection can be much more useful in certain scenarios.

Adomas Šulcas
4 min read
What is an Ethernet Connection?
An ethernet connection is created by attaching a specific cable (typically, Cat5e or Cat6e) to a machine that has ethernet ports. Multiple devices connected with ethernet cables form a Local Area Network (LAN) and can interact with each other through that method.
While LAN isn’t as popular or as useful anymore, it used to be widely used in confined spaces to deliver data and perform other actions quickly. LAN is still beneficial in some use cases, although regular internet users will rarely take advantage of all of the features.
Wired connections in general are more difficult to implement since they heavily restrict device mobility. Mobile devices, for example, lack ports for wired connections as using ethernet cables would defeat a major benefit of the device.
These drawbacks do come with some benefits, however. Primarily, it’s faster internet speeds and a more consistently solid connection to the internet. A wired ethernet connection will usually be faster than an identical wireless connection while also offering better stability.
The reasons are simple – ethernet cables are not subject to signal degradation or interference and they are also additionally shielded from EMI. As long as the cable itself is not harmed, no degradation will occur on a physical level, although if the Internet Service Provider experiences technical issues, then the connection will falter as well.
Additionally, ethernet cables provide a direct path from device to device, reducing overall signal latency. Wi-Fi establishes a common connection as well, you can find device name by Mac address in both cases, but interlinking devices with cables is much more reliable.
Due to all these and many more reasons, an ethernet connection is preferred where reliability and maximum speeds are preferred such as service infrastructure, streaming, or even gaming.
What is Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi (or Wireless Fidelity) is a way to connect devices to the internet without using ethernet cables on each one. In most cases, the Wireless Access Point (WAP) will be using an ethernet cable for its own internet connection.
There are exceptions to this such as when several WAPs are communicating with each other, although at least one needs to have an ethernet connection.
Once a connection is established, the WAP uses radio waves to transmit signals to other devices. These signals are based on a specific standard so that all devices with Wi-Fi capabilities may connect to the WAP. Older devices use WAP2 vs WPA3 is used in newer ones.
There’s a few more stages to connecting to wireless networks, but most of them happen on the software layer (such as the establishing of an SSID and exchange of security credentials).
One of the greatest benefits that Wi-Fi provides is the ability to connect multiple devices wirelessly. Such flexibility made the technology explode in popularity and it’s now in almost every home, restaurant, and office building in existence.
There are some drawbacks to Wi-Fi, however. First, it’s not as reliable as a wired ethernet connection as radio waves tend to get interfered with and experience degradation, especially when they have to go through solid objects.
Part of the issue is fixed by implementing repeaters and signal boosters, but the issue always remains. Additionally, the WAP shares the same bandwidth with all devices at once. So, if you have dozens of mobile devices connected to the same access point, internet speed will be significantly downgraded.
For similar reasons, Wi-Fi is also less secure than ethernet connections as it's much easier for third parties to connect and intercept the data. That's why use a VPN on public Wi-Fis is strongly recommended (check are VPNs legal in your country before).
Network administrators might restrict Wi-Fi connections more, so usually, wireless users have fewer permissions to tinker with settings. Various online actions might not be possible, as well as VPN not connecting so fast.
Ethernet vs Wi-Fi: Differences
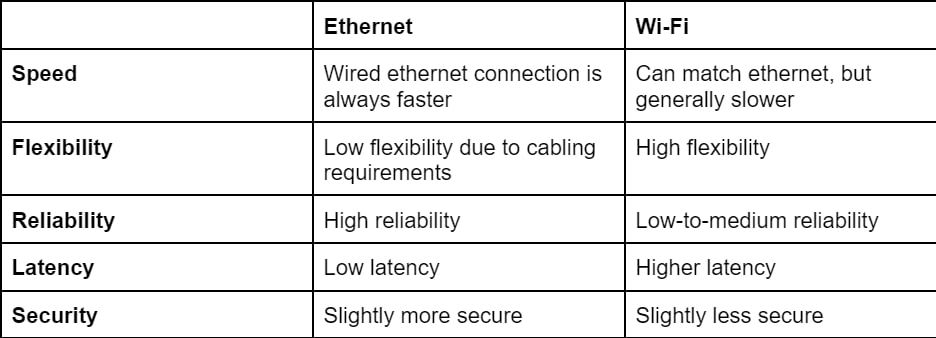
In general, ethernet is the all-round better way to connect to the internet with the major drawback being that all devices need cables. As such, for cases where you don’t need to squeeze out the maximum speed and reliability, Wi-Fi is the easier choice.
So, when considering ethernet vs Wi-Fi, the primary aspect is whether you absolutely need all the reliability, security, and slightly better speed that ethernet provides. If you’re just planning to use the internet for regular home activities, there’s no reason to use ethernet cabling.
On the other hand, if your machines run important services, you intend to play highly competitive games, or perform other activities where even a second of downtime could be impactful, ethernet is the only choice.

Author
Adomas Šulcas
Chief Operating Officer at Growth Bite
Adomas is a technical writing expert who founded Growth Bite, a digital marketing company, focused on providing high-value SEO and content marketing services to SaaS companies.
Related articles
4 min read
Best Residential VPN Providers in 2025
A Virtual Private Network (VPN) encrypts your traffic and hides your IP address. The way these functions are accomplished affects various aspects of your online privacy and security.
Here, we'll consider using residential IP addresses instead of those originating from a data center. A residential VPN has advantages compared to traditional ones, but there are some caveats.
It all boils down to residential VPN providers. The worst ones may even create more risks than benefits. We'll end this article with a list of the best residential VPN providers on the market.

Guoda Šulcaitė
4 min read
Ethernet vs Wi-Fi: Which One is Better?
Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two main ways to connect your computer to the internet. While Wi-Fi has received significantly more attention in recent years, especially among consumers, due to its simplicity and flexibility, ethernet is still widely used in various other applications.
Even if Wi-Fi is significantly more popular, it isn’t strictly better. Both methods have their benefits and drawbacks. Wi-Fi’s popularity comes from its ease-of-use and flexibility, but an ethernet connection can be much more useful in certain scenarios.

Adomas Šulcas
5 min read
How to Change Chrome Proxy Settings: The Ultimate Guide
A proxy server is an easy alternative to a VPN that can perform most of the functions of the latter. It’s a server that stands between your device and the destination server, taking your connection requests and forwarding them in your name.
Destination servers in almost all cases see the proxy server as the originator of the request. As such, proxies are widely used in various, mostly business-related applications whenever privacy, security, location changing, and several other factors are at play.

Guoda Šulcaitė