WPA2 vs WPA3: Which is Better for Your Wi-Fi Security?
Wi-Fi security protocols are there to keep your devices safe from cyber threats. Hackers are always on the lookout to steal someone’s data and use it to their advantage. As a result, it endangers your private and sensitive information such as email, phone number, and bank details.
That’s where WPA2 and WPA3 step in. These powerful network security protocols guard your online world. They shield you from hackers and keep your digital presence safe. In this article, you will learn what these protocols are, how they compare, and why they’re essential.

Guoda Šulcaitė
6 min read
What are WPA 2 and WPA3?
What is WPA2?
WPA2 has been a top security standard for wireless networks for many years. It replaced the older WPA protocol and brought stronger protections to keep networks safe.
The system uses Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) for robust data encryption. It also supports TKIP for backward compatibility, which helps older devices connect more easily.
Even though it’s much more formidable than the previous WPA security protocol, WPA2 is still vulnerable to brute-force attacks that try to guess passwords by entering many different combinations quickly.
What is WPA3?
WPA3 represents the latest breakthrough in the history of encryption for Wi-Fi security protocols. It tackles the security gaps found in the older WPA2 protocol, creating more robust defense for modern networks.
The new system brings several powerful features to keep your data safe. Here are some of them:
- Simultaneous Authentication of Equals (SAE). It helps verify devices more secure than ever before.
- Forward secrecy. Even if someone steals encryption keys, they can’t unlock past communication sessions.
- 192-bit encryption. Especially useful for businesses that need extra protection, 192-bit encryption offers enterprise-grade security that’s difficult to break.
Worth noting that the two latter features are also why individuals and businesses use Virtual Private Networks. Learn more in our article on why use a VPN service.
Why Do These Protocols Matter?
Wi-Fi security protocols are more than just technical details. As noted in our internet connection encryption guide, WPA2 and WPA3 protect your personal and professional digital spaces from dangerous cyber threats and unauthorized access.
Everyday users depend on these systems to keep their online information private and secure. Businesses, on the other hand, rely on these network security protocols to shield sensitive business data from cyber attacks.
WPA2 vs WPA3: Key Differences
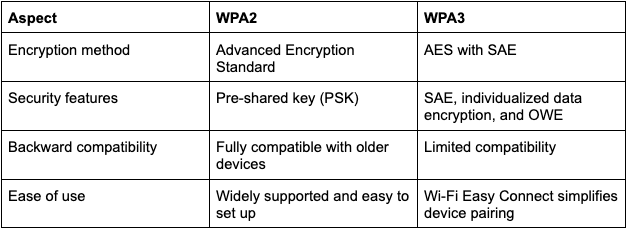
Encryption Standards
WPA2 uses Advanced Encryption Standard to lock down data securely. Its reliance on pre-shared keys can create weak spots that clever hackers could exploit.
WPA3 makes big improvements by introducing SAE, which removes shared keys altogether and makes encryption much stronger. As a result, it becomes more difficult for cybercriminals to hack into your device.
Device Authentication
The older WPA2 protocol depends on a pre-shared key (PSK) for verifying devices. WPA3 completely changes that by replacing the pre-shared key with SAE, which provides a powerful shield against unauthorized access. These upgrades make it much harder for hackers to break into wireless networks.
Protection Against Cyberattacks
WPA2 leaves wireless networks vulnerable to several dangerous hacking techniques and threatware. Brute-force and dictionary attacks can slip past its defenses relatively easily.
WPA3 brings powerful new tools to fight these digital threats. Its advanced encryption methods and forward secrecy create a much stronger shield against hackers.
Ease of Use for Home Wi-Fi Networks
WPA3 simplifies the setup of IoT devices and allows faster and more secure connections. Unlike WPA2, which demanded manual settings and configurations, the newer protocol enables homeowners to set up and protect their network with much less hassle.
Security Improvements in WPA3
Protection Against Offline Dictionary Attacks
WPA3 creates a powerful defense against common hacking tricks. Dictionary attacks, which try to guess passwords using common word lists, become almost useless against this protocol.
Additionally, WPA3 makes it incredibly difficult for attackers to crack encryption keys and your wireless network gains a much stronger shield against cyberthreats.
Forward Secrecy
Forward secrecy is a game-changing protection method implemented in WPA3. If someone somehow steals encryption keys, they still cannot unlock past communication sessions.
It becomes crucial when protecting sensitive information that passes through wireless networks. Forward secrecy creates an extra layer of security that keeps your sensitive data exchanges safe from prying eyes.
Enhanced User Privacy on Public Wi-Fi Networks
Public Wi-Fi networks have always been risky and dangerous, there’s no doubt about it. Hackers can easily steal information from unprotected connections.
WPA3 changes this dangerous situation by creating individualized data encryption. It means that even if someone is on the same Wi-Fi as you, they can’t read your specific and unique data traffic.
As a result, users can feel safer when connecting to shared Wi-Fi networks, knowing their personal information remains protected. WPA3 gives people a private digital space even in crowded public spots.
Which Should You Choose: WPA2 vs WPA3?
For Home Users
WPA3 offers the best protection for home networks today. It provides stronger wireless network security that keeps your digital life safer. Older devices might still work better with WPA2, so check your equipment before making a switch.
Most modern routers and devices now support the newer, more powerful WPA3 network security protocol.
For Businesses
Businesses need top-level network protection at all times. WPA3 delivers advanced security that shields confidential data from potential cyberthreats. Its powerful encryption and forward secrecy make it the ideal choice from companies handling sensitive information.
Businesses can’t afford to take risks with their digital security, so it’s imperative that they go with the newest WPA3 protocol.
For IoT and Smart Devices
WPA3 makes connecting smart devices easier and safer than ever. Its streamlined approach creates smooth and secure setups for IoT technology. Individualized data encryption protects each device and gives users peace of mind about their smart home networks.
When WPA2 Might Be Good Enough?
WPA2 still works well for networks with older equipment. You can boost your protection by choosing strong passwords and keeping the firmware up to date at all times.
This approach will help you maintain solid Wi-Fi security even with WPA2. Smart router management could also help close potential security gaps.
How to Upgrade to WPA3: A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Check Compatibility
- Routers. Routers need special support for WPA3. Check your router’s manual or website to confirm its capabilities (you might need to find device name by MAC address for that). Most newer routers can handle a more advanced Wi-Fi security protocol. If you’re unsure, contact the manufacturers for help.
- Devices. Devices matter, too. Smartphones and laptops made after 2020 usually support WPA3. Look at your device specifications. Not all gadgets work with the newest wireless network security system.
2. Update Router Firmware
Getting into your router's settings takes a few steps:
- Open a web browser.
- Type in your router’s IP address into your web browser.
- Enter your login information.
- Find the “Firmware” or “Update” section.
- Download the latest firmware update.
- Restart the router.
Updates can add WPA3 features to your existing equipment.
3. Configure WPA3 Settings
Look for the wireless security section and choose WPA3-Personal as your authentication method. Some routers may offer a mixed mode (WPA2/WPA3) that works with both new and old devices.
Setting up SAE requires a strong password. WPA3 replaces old wireless security methods with this advanced protection. Create a unique password that’s hard for hackers to guess. Mix uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special symbols to build a strong password for your network.
WPA2 vs WPA3: Final Words
If we had to choose between WPA2 and WPA3, WPA3 stands as the champion of wireless network security. It brings powerful new tools and features to protect your online presence. WPA2 and the pre-shared key served us well, but the time has come for this newer, much stronger protocol. Individualised data encryption and advanced features like SAE create a tough shield against cyber threats.
For homes, businesses, and smart devices, WPA3 delivers top-level protection. Not all older equipment works with this wireless network security protocol, but newer devices get robust wireless security.

Author
Guoda Šulcaitė
Growth Manager at CometVPN
Guoda is an all-round marketing professional with deep knowledge in the tech SaaS industry, particularly VPNs and proxies. She has worked on numerous projects and helped achieve impressive results through project management, content production, and SEO.
Related articles
4 min read
Ethernet vs Wi-Fi: Which One is Better?
Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two main ways to connect your computer to the internet. While Wi-Fi has received significantly more attention in recent years, especially among consumers, due to its simplicity and flexibility, ethernet is still widely used in various other applications.
Even if Wi-Fi is significantly more popular, it isn’t strictly better. Both methods have their benefits and drawbacks. Wi-Fi’s popularity comes from its ease-of-use and flexibility, but an ethernet connection can be much more useful in certain scenarios.

Adomas Šulcas
5 min read
How to Change Chrome Proxy Settings: The Ultimate Guide
A proxy server is an easy alternative to a VPN that can perform most of the functions of the latter. It’s a server that stands between your device and the destination server, taking your connection requests and forwarding them in your name.
Destination servers in almost all cases see the proxy server as the originator of the request. As such, proxies are widely used in various, mostly business-related applications whenever privacy, security, location changing, and several other factors are at play.

Guoda Šulcaitė