pDoS Attacks: What They Are and How to Prevent Them
Denial of Service (DoS) attacks disrupt access to networks or services. But a more harmful variant is pDoS, or Permanent Denial of Service. Unlike other DDoS attacks that flood the target with huge amounts of internet traffic, a pDoS attack can permanently damage hardware.
Understanding Permanent Denial of Service is crucial since these types of attacks target the hardware layer, not just software. In this blog post, you will learn how a pDoS attack works and how to prevent long-term damage and costly recovery.

Adomas Šulcas
4 min read
What is a pDoS attack?
A pDoS attack is what the name says – a Permanent Denial of Service. It can “brick” your device, making it permanently unusable, hence the name. Attackers may corrupt firmware to damage the hardware and render it useless.
Key terms:
- Permanent Denial of Service. An attack that permanently damages hardware.
- Phlashing. A method of a pDoS attack that replaces firmware with corrupted images that turns the device useless.
- Firmware. Software (also known as system software or microcode) in hardware, which can be vulnerable in case of a pDoS attack.
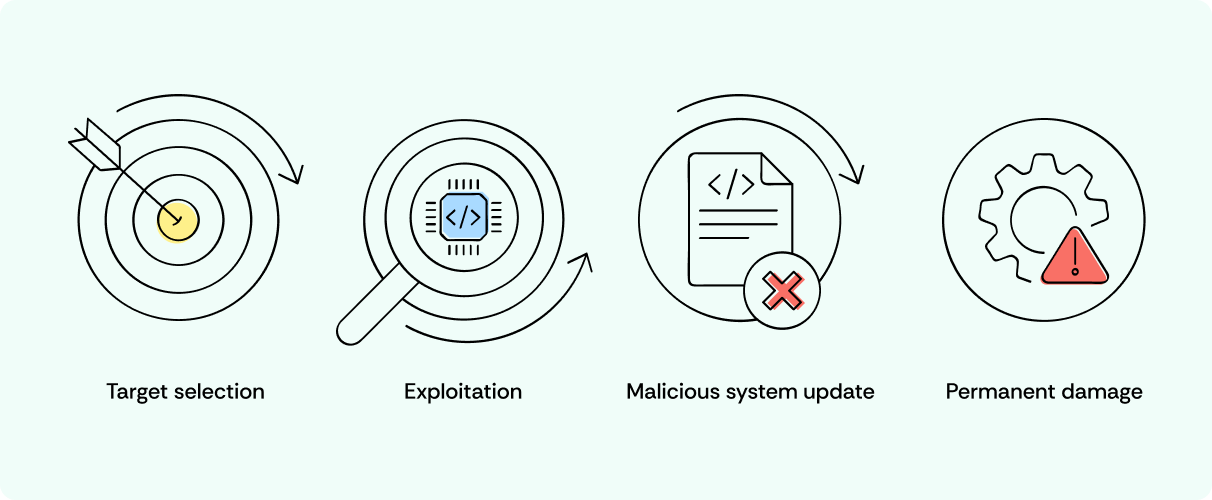
How Do pDoS Attacks Work?
- Target selection. Attackers target devices with outdated or insecure system software.
- Exploitation. They find and exploit vulnerable firmware.
- Malicious system update. Attackers send a malicious update to corrupt the microcode.
- Permanent damage. The device basically becomes a “brick” – permanently nonfunctional.
Common Attack Vectors
- Vulnerabilities. Unpatched firmware is a common entry point.
- Malicious updates. Fake system software updates overwrite critical systems.
- Hardware exploits. Some attacks exploit hardware design flaws.
Real-World pDoS Attack Examples
Throughout modern history, there have been many attempts at pDoS attacks. Here are some of them.
Remaiten
Remaiten is a type of malware found in 2016. It targets IoT devices, especially Linux on embedded systems like routers. Remaiten stands out for how it infects IoT devices. It uses remote access, mostly by exploiting weak telnet passwords.
After infecting a device, Remaiten can do many things – from performing system-level actions to downloading malware and removing other bots on the infected system. Also, it can disable a router’s network. All this makes the device unusable until it’s factory reset.
Silex
Having emerged in 2019, it targets Linux systems and IoT devices and has multi-vector destructive capabilities. After gaining root access, Silex corrupts storage, wipes files, deletes firewall rules, and more. As a result, the device becomes completely non-functional.
The malware causes system-wide disruptions and often requires complete replacement of all hardware.
Bad Rabbit
Bad Rabbit is a pDoS malware detected in 2017. It blends ransomware and destructive tactics. It infects systems through a fake Adobe Flash installer and spreads using hardcoded SMB credentials and Mimikatz. It encrypts files and the MBR and makes the systems unbootable.
This dual attack is what sets Bad Rabbit apart from typical ransomware. The MBR encryption means that data backups aren’t enough. It propagates rapidly and targets high-profile organizations. Its sophistication, including legitimate tool misuse, marks it as a formidable pDoS threat.
The Consequences of pDoS Attacks
As mentioned before, a pDoS attack can cause long-lasting, costly impacts. Here are some of them:
- Financial losses. Replacing damaged hardware is extremely expensive, depending on the scale of phlashing.
- Operational downtime. Essential equipment can take days, weeks, or even months to restore.
- Reputational damage. As a cherry on top, phlashing can seriously hurt customer trust. Unlike other attacks, it requires hardware replacement, not just some minor software fixes.
How to Protect Against pDoS Attacks?
At this point, you’ve seen how bad it is to be on the receiving end of a pDoS attack. While there isn’t a single method to prevent them altogether, you can do several things to keep your cyber-hygiene in check to minimize the chances of it happening:
- Updates. Regularly update your system software to patch any vulnerabilities.
- Antivirus software. New viruses appear every day, so it’s essential that you install and keep your antivirus software up to date.
- Network monitoring. Use Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) to spot unusual activity. It could help prevent a pDoS attack.
- Secure hardware. Choose devices with security in mind, especially IoT devices.
- Ensure strict company policy. Make sure that you know everyone that has access to company’s offices and forbid people from using personal USB sticks on company property.
- Incident response plan. Disconnect affected devices immediately to contain spread.
These measures, especially system software updates, reduce pDoS attack risk. Securing hardware and monitoring networks help avoid these damaging attacks.
So, if you’re seeing symptoms such as slow PC speed, files not opening like they used to, trouble connecting to websites, or a complete disconnection from the internet, be prepared to deal with a potential pDoS attack.
However, don’t jump to conclusions immediately. Take precaution and make sure that’s the case before spreading panic and taking extreme measures.

Author
Adomas Šulcas
Chief Operating Officer at Growth Bite
Adomas is a technical writing expert who founded Growth Bite, a digital marketing company, focused on providing high-value SEO and content marketing services to SaaS companies.
Related articles
4 min read
Ethernet vs Wi-Fi: Which One is Better?
Ethernet and Wi-Fi are the two main ways to connect your computer to the internet. While Wi-Fi has received significantly more attention in recent years, especially among consumers, due to its simplicity and flexibility, ethernet is still widely used in various other applications.
Even if Wi-Fi is significantly more popular, it isn’t strictly better. Both methods have their benefits and drawbacks. Wi-Fi’s popularity comes from its ease-of-use and flexibility, but an ethernet connection can be much more useful in certain scenarios.

Adomas Šulcas
5 min read
How to Change Chrome Proxy Settings: The Ultimate Guide
A proxy server is an easy alternative to a VPN that can perform most of the functions of the latter. It’s a server that stands between your device and the destination server, taking your connection requests and forwarding them in your name.
Destination servers in almost all cases see the proxy server as the originator of the request. As such, proxies are widely used in various, mostly business-related applications whenever privacy, security, location changing, and several other factors are at play.

Guoda Šulcaitė